For context, this "explainer" is presented without respect to specific application requirements.
A UPS (Uninterruptable Power Supply) manages power and load conditions supplied by branch circuits, post-panel, referred to as “demand-side”. While an auxiliary power source manages transition and supply of electrical utility from one source of power to another that feed the “mains” pre-panel, referred to as “supply-side”.
Often conflated in general discourse; each system serves distinctly different power management requirements. They are designed to work either alone, or in concert with each other to provide a seamless, non-disruptive experience for building systems, and specifically, datacenter, network and information systems.
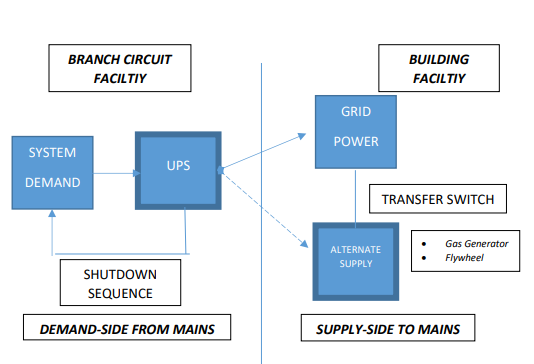
In either use case, a UPS is online and reacts to power quality without regard to the source and in real-time. The UPS will begin coordinated shutdown of systems prior to exhaustion of its batteries. The alternate supply; however, must be “switched-in” either automatically or manually when a primary source is interrupted. As the alternate source is generally not “online” when an outage occurs, switching may result in delay during the transfer process. A UPS will compensate for reasonable delay in absence of additional supply-side and transfer switching failure modes.
PSFA employs UPS technologies within its datacenter, network and information system design; however, the building plant is not equipped with an alternative power source. Under nominal circumstances, the PSFA datacenter may operate for up to one hour during the course of systems shutdown; however, some services will become unavailable as early as 20 minutes into the shutdown sequence.
By: K. Gray, CTO/CIO, PSFA Revised 14NOV2023